Settings
Settings and keywords
At this point, we can look at where the methods used for different tasks are actually defined.
If we want to use the best-known methods for certain applications, or the methods with the best cost-benefit ratio, there is no single method that can be used for all purposes. Different methods are needed for different applications. In addition, expert users may want to define their own configuration files to use their own set of methods.
In order to standardize the methods used to perform quantum chemistry calculations, but at the same time provide enough flexibility for individual applications, experimental settings, and various user-specific needs, we use a hierarchy of configuration options:
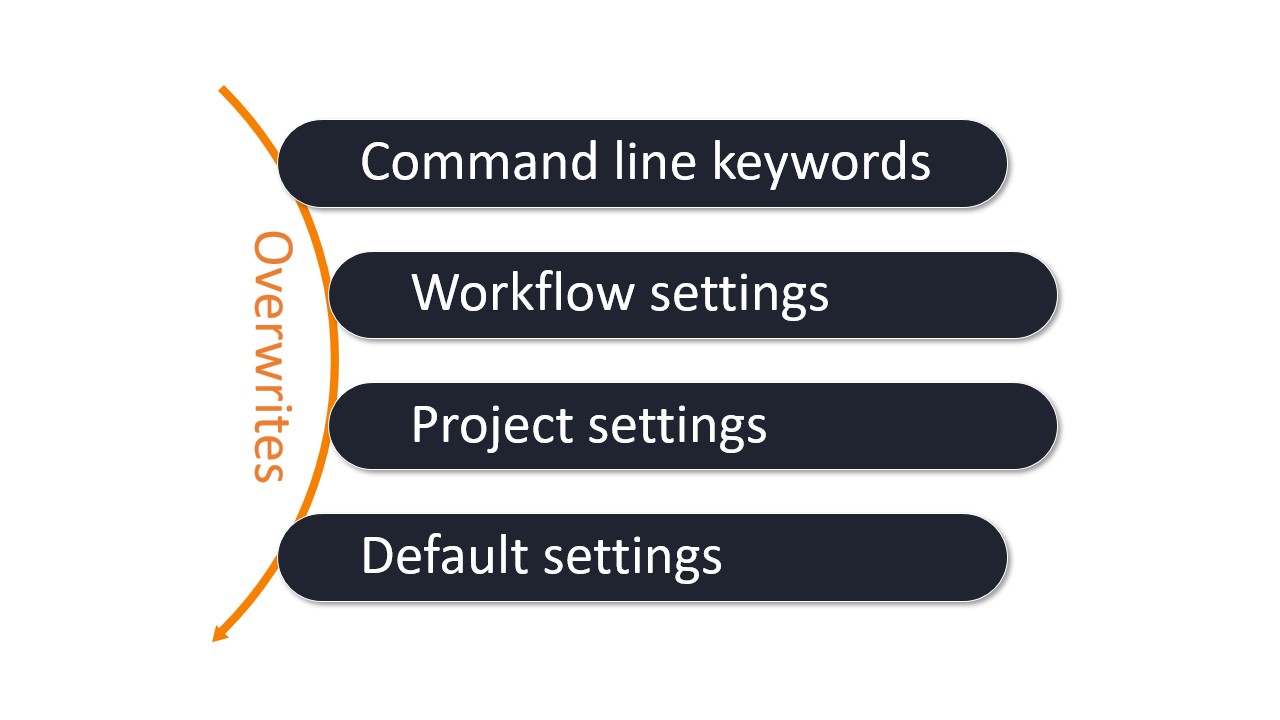
Hierarchy of settings and options used for a WEASEL job.
Command line keywords: The command line keywords are used when starting WEASEL. Here the default methods and settings are overwritten, e.g. methods used for specific tasks, solvents or system charges.
weasel water.xyz [KEY1] [KEY2] ...
Workflow settings: The workflow settings are used for standard workflows, and are stored in a configuration file. The workflow configuration files are provided together with the standard WEASEL release, but can also be developed together with FAccTs or by the users themselves for their local applications.
weasel water.xyz -workflow <workflow name>
Project settings: The project settings are used for project-specific or user-specific settings, and are also stored in a configuration file. The project settings can be easily copied and modified from the default
settings.inifile. They can be quite useful for expert users.
weasel water.xyz -settingsfile mysettings.ini
Default settings: The default settings are stored in a configuration file. These settings are used if e.g. WEASEL is called solely together with a structure file or if an option has not been set by any of the aforementioned interfaces:
weasel water.xyz
Important
Most of the defaults defined in the configuration files can be overwritten via arguments in the command line.
Important
All settings and workflows are version bound to a minor version of WEASEL (i.e., 1.10 or 1.11, ...) as keywords might be changed, removed or added between versions.
Therefore, settings files use following name scheme: settings-1.11.ini, where 1.11 is the minor version of WEASEL.
Furthermore, all settings and workflow files must contain following keyword:
[SOFTWARE]
# Minor version of WEASEL. See example below
Version = 1.11
Settings files
Default settings
WEASEL's built-in default settings can be customized by creating a
system settings file /etc/weasel/settings-1.11.ini or a user settings
file ~/.config/weasel/settings-1.11.ini while the values in the latter
one take precedence. For running WEASEL some mandatory minimal settings
are required (see here for details). For
convenience, all built-in default settings are documented with
explanatory comments: weasel-<version>/settings/defaults.ini
This file has the format of a configuration file, containing sections with their keys (name-value pairs), here shown for the preoptimization step:
[PREOPT]
# True if preoptimization is the default, else False
Default = True
# Options HF-3c, PBEh-3c, XTB
Method = XTB
The above keys define that, by default, the basic workflow includes the preoptimization task - in which the XTB method (GFN2-xTB) is used.
Note
Note, the path of the system settings file /etc/weasel/settings-1.11.ini
can be customized by the environment variable WEASEL_SYSTEM_SETTINGS.
Project settings
Project settings files or personalized settings files can be defined and
used as a replacement to the settings.ini file described above. Such
a project settings file is added via the command line:
weasel water.xyz -settingsfile /path/to/mysettings.ini
The project settings does not differ from the default settings which are
documented in weasel-<version>/settings/defaults.ini. Just the
values can be different.
Note
The project settings file can be useful if a project requires different settings from the defaults. Alternatively, experienced users might have different preferred calculations, which they can then define in their own project settings.
Important
The values from the project settings only overwrite the values from the default settings. I.e. if keys or entire sections are missing in the project settings, they are simply taken from the default settings. This can be useful if e.g. the paths to software used by WEASEL are always the same, or if the project settings is from an older version compared to the default settings from a newer release - which usually contains new keys.
Workflow settings
The workflow settings files have the same format as the default and project settings files.
The workflow settings files are stored in:
weasel-<version>
├── workflows
│ ├── workflow_exploreReactivity.ini
│ ├── workflow_IR.ini
│ ├── workflow_NMR.ini
│ └── ...
A workflow settings file does not differ from the default settings which are
documented in weasel-<version>/settings/defaults.ini and can also be viewed as a project settings file. It is just that the values can be different and usually the workflow settings files contain
fewer sections compared to the default settings file: the workflow settings files only contain those sections, that are necessary for the particular workflow. Values for the missing sections are taken from the default or project settings.
Note
Workflow settings can be combined with project settings. The project settings overwrite the default settings, and the workflow settings overwrite the combination of project and default settings.
Important
We try to keep the workflow files forward compatible, so that once established workflow files can be used with new WEASEL versions as well.
Sections in settings files
We briefly discuss the most important sections in the settings file.
The preferences file is divided into several sections. To view the contents of each section, click its name in the list:
Note
Possible values for the methods, basis sets, solvents, ... defined in the sections can be listed with the command
weasel -h
SOFTWARE
All information related to the back engine(s) of WEASEL.
For WEASEL-1.11 this part contains the following:
[SOFTWARE]
# To which weasel version does this settings file belong to. Do not change!
Version = 1.11
# Give full path to orca
ORCA_PATH =
# Path to GOAT binaries
GOAT_PATH =
# Give full path to openmpi - lib and bin should be subdirectories of that path
MPI_PATH =
# Give executable of crest with full path.
CREST_EXEC =
# Set rsh command for parallel Weasel runs on clusters
RSH_COMMAND = ssh -x -v
# Set rsh connection timeout for parallel Weasel runs on clusters (unit: seconds) [default: 15]
RSH_TIMEOUT = 15
# Set number of tries for rsh connection test
# For value <= 0 the connection test will be disabled
RSH_TRIES = 5
# Optional: Set scratch directory for WEASEL jobs. Leave unset for using the current directory of a job.
SCRATCH_DIR =
# Optional: List of environmental variable names, that are ensured to be set on every node by Weasel. Listed variables
# have to be set on the head node, otherwise they are ignored.
# (e.g. ENV_VARS=OMPI_MCA_btl_tcp_if_include,OMPI_MCA_btl_tcp_if_exclude,OMPI_MCA_btl)
ENV_VARS =
# Optional: Set backing scratch directory for Open MPI, which is used as fallback in case the usual
# scratch dir runs out of space.
OPENMPI_BACKING_DIR =
HARDWARE
All information related to available hardware. How many cores can be used, how much memory is available. Part of this has already been discussed here.
For WEASEL-1.11 this part of the settings.ini file contains the following:
[HARDWARE]
# Memory available per core.
# Following SI unit suffixes are allowed: B, K, M, G, T [default: M], e.g. 1G
# Units are interpreted as powers of 1000 (SI format).
# Example: If 4 cores (pal4) are used and in total 32000 MB RAM is available, Memory should be set to 6000
Memory =
# Set the total memory of the current machine. This option is mutually exclusive to "Memory".
# The same rules as for the "Memory" option apply.
MemoryTotal =
# Ratio of available memory allocated to ORCA calculation, should be between 0 and 1. The developer team recommends
# to use only 75%, i.e. 0.75, of physically available memory.
MemoryRatioForORCA = 0.75
# Number of cores to be used for parallel jobs
Cores =
# Allow using hyper-threading [default: False]
Use_Hyperthreading = False
# Enable Intel MKL performance boost for non-Intel CPUs (only available on Linux systems) [default: True]
Boost_NonIntel = True
# Maximum number of cores for a single ORCA calculation.
# Disable by choosing value < 1.
# (Option is mandatory)
MaxCoreOrca = 32
# Maximum number of cores for a single numerical Hessian (!NumFreq) ORCA calculation.
# Disable by choosing value < 1
# (Option is mandatory)
MaxCoreOrcaNumFreq = 120
PREOPT
The preoptimization step is switched on by default. It is included for computational efficiency. A cheap preoptimization can safe later more expensive optimization steps. The method for preoptimization is defined here:
[PREOPT]
# True if doPreOpt is the default, else False
Default = True
# Options HF-3c, PBEh-3c, XTB
Method = XTB
# True if PreOpt should not change the topology (non-hydrogen bonds) of the structure.
KeepTopology = True
OPT
The optimization step (DFT, semiempirical, or wavefunction) is switched on by default. Its method with accompanying basis set is defined here. Is a frequency run carried out after geometry optimization? At what value does an imaginary frequency indicate a saddle point? How many number of steps are per default used for relaxed surface scans?
This looks like this in the settings.ini file:
[OPT]
# True if doOpt is the default, else False
Default = True
# Options BP86, B3LYP, B3LYP, MP2, XTB, ... see methodOpt
Method = r2SCAN-3c
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis = def2-TZVP(-F)
# Options: None (no basis2 for optimization) or see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis2 = def2-TZVP
# Options: any integer
ScanNSteps = 10
# If by default after each optimization a frequency calculation should be run --> True, otherwise False
FreqAfterOpt = False
# If by default after each TS optimization a frequency calculation should be run --> True, otherwise False
FreqAfterOptTS = True
# Threshold for checking for imaginary modes in frequency output. Imaginary frequencies above this threshold
# are not considered as imaginary modes when checking for the nature (minimum or TS) of the stationary point.
threshImagMode = -5
# Threshold for checking for imaginary modes in frequency output. Imaginary frequencies below this threshold
# are considered as critical imaginary modes when checking for the nature (minimum or TS) of the stationary point.
threshImagModeCritical = -20
# Use the default grid (<BLANK>) or a finer grid (DefGrid3) for the optimization. Options: DefGrid1, DefGrid2, DefGrid3
Grid =
# Which thresholds to use for optimization. Options are: Loose, Normal, Tight, VeryTight
OptType = Normal
# If frequency calculation is carried out, rerun optimization in case (unwanted) imaginary modes are found with the
# frequency analysis. If frequency calculation is not carried out, this keyword is ignored.
# Options are: True, False
CorrectImagModes = False
# How many optimization reruns should be run if (unwanted) imaginary modes are found
NReRunsCorrectImagModes = 3
# Calculate exact initial Hessian before optimization?
CalcInitialHess = False
# Try to converge a non-converged geometry optimization by running a few more optimization cycles.
# Also see the option: 'CONFORMATIONAL_SEARCH->OptRetry', which overrides this setting within the
# conformer search procedure.
# Options: 'True' or
SP_DFT
The final single point energy calculation at DFT level (all rungs of Jacob's ladder) is switched on by default. Its method with accompanying basis set is defined here:
[SP_DFT]
# True if doSP_DFT is the default, else False
Default = True
# Options: BP86, B3LYP, RIJK-B3LYP
Method = wB97X-V
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
# Not used if composite methods are used, but needed in case a non-composite method is chosen.
Basis = def2-TZVP
# Options: None (no basis2 for SP_DFT) or see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis2 = def2-QZVPP
# Use the default grid (<BLANK>) or a finer grid (DefGrid3) for SP_DFT calculation. Options: DefGrid1, DefGrid2, DefGrid3
Grid =
# SCF Convergence criteria to be used for SP_DFT calculation. Use the default convergence (None) or other criteria.
# Options: None (default), SloppySCF, LooseSCF, NormalSCF, TightSCF, VeryTightSCF, ExtremeSCF.
SCFConv = None
# Compute gradient on SP_DFT level. True or false.
Gradient = False
SP_WF
The final single point energy calculation at wavefunction level is switched off by default. (Switch on typing -spwf)
Its method with accompanying basis set is defined here.
For DLPNO-methods the default PNO setting is also defined in this section:
[SP_WF]
# True if doSP_WF is the default, else False
Default = False
# Options: MP2, RI-MP2, RIJK-RI-MP2, RIJCOSX-RI-MP2, DLPNO-MP2, RIJK-DLPNO-MP2, RIJCOSX-DLPNO-MP2,
# CCSD(T), RIJK-CCSD(T), DLPNO-CCSD(T), RIJK-DLPNO-CCSD(T), RIJCOSX-DLPNO-CCSD(T)
Method = DLPNO-CCSD(T)
# Options: def2-SVP, def2-TZVP, def2-TZVPP, def2-QZVP, def2-QZVPP,
# ma-def2-SVP, ma-def2-TZVP, ma-def2-TZVPP, ma-def2-QZVP, ma-def2-QZVPP,
# cc-pVDZ, cc-pVTZ, cc-pVQZ, cc-pVZ5, cc-pV6Z,
# aug-cc-pVDZ, aug-cc-pVTZ, aug-cc-pVQZ, aug-cc-pV5Z, aug-cc-pV6Z
Basis = def2-TZVP
# Options: None (no basis2 for SP_WF) or see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis2 = def2-QZVPP
# PNO Settings for DLPNO calculations.
# Options: Loose, Normal, Tight, Normal_TightPairs, LooseIntra_NormalTightPairsForInteraction, LooseIntra_TightForInteraction, NormalIntra_NormalTightPairsForInteraction, NormalIntra_TightForInteraction
PNOSetting = Normal_TightPairs
# Use the default grid (<BLANK>) or a finer grid (DefGrid3) for the SP_WF calculation. Options: DefGrid1, DefGrid2, DefGrid3
Grid =
# Solvation method used for post-HF calculations.
SolvMethod = PTE(S)
PRE_SCF
This section is defined as following:
[PRE_SCF]
# Options: True, False
DoPreSCF = True
SCF_CONVERGENCE
This section is defined as following:
# Try to recover a non-converged SCF calculation by using different SCF accelerators strategies (for more details
# see the setting 'BadConvLevel' below).
# IMPORTANT: This option is turned off when 'SCF_CONVERGENCE->BadConvLevel' is set.
# Options: 'True' or 'False'
Retry = False
# Triggering convergence accelerator strategies for systems that are difficult to converge.
# IMPORTANT: Turning on this option will turn off automatic SCF retries (see setting 'SCF_CONVERGENCE->Retry')
# For details about the individual strategies see: weasel -h
# Options:
# <Blank>: Turned off. No specific convergence accelerators is used by default.
# <integer between 1-4>: Turn on level 1, 2, 3 or 4 convergence accelerators.
BadConvLevel =
RELATIVISTICS
Should ECPs be used, or a relativistic method? Starting from which atomic number should relativistic methods be used?
This section is defined as following:
[RELATIVISTICS]
# Options: ZORA, DKH, ECP, None
# ZORA and DKH, if defined here, are only used if the system contains elements with an atomic number >= UseScalarRelFromAtomicNumber
# ECPs, if defined here,are only used for those elements in the system that have an atomic number >= UseECPsForElementFromAtomicNumber
Method = ECP
# If Method == ECPs or if -ecp is chosen, which ECPs are to be used. Options are def2-ECP and SDD
ECP = SDD
# If Method above is ZORA or DKH, only use that method if the system contains at least one atom with at least the given atomic number
UseScalarRelFromAtomicNumber = 21
# Use ECPs for those elements starting from atomic number
# Info: def2-ECPs are available starting from Rb(37). Recommended together with def2 Karlsruhe basis sets.
# SDDs are available starting from Li(3). However, we would recommend to start using SDD from the 1st transition metal Sc(21).
UseECPsFromAtomicNumber = 21
PLOTS
Which output format should be used for MO, density and Fukui plots? The grid resolution and box size are defined here. For plotting SOMOs, should they be localized by default?
This section is defined as following:
[PLOT]
# Options: Integer. Default from ORCA is
# Grid resolution per Angstrom. Is applied to all directions. Alternatively, gridx, gridy, gridz can be defined individually via the command line
# Should be a positive integer or float.
GridResolution = 5
# Options: cube, vis (Maestro - Schroedinger)
OutputFormat = cube
# Dimensions for the plot. Options: default: ORCA will set the dimensions from the molecular geometry.
# First a box hat contains all atoms is constructed. Then 7 Bohrs are added in each direction.
# Alternatively define the dimensions here (in Angstrom) or via the command line.
XMax = default
XMin = default
YMin = default
YMax = default
ZMin = default
ZMax = default
# Defines the default box dimensions. Box is constructed such that the planes have at least 'BoxAddToAtoms' Bohr distance to all atoms.
# Should be a positive integer or float.
BoxAddToAtoms = 7
LocalizeSOMOs = True
#
# This is now the spectrum plot part
#
# Linewidth (full width at half maximum) of plotted spectra in eV (TDDFT), Hz (NMR), or 1/cm (IR/Raman)
Linewidth = 0.5
# Lineshape function: 'Gaussian' or 'Lorentzian'
Lineshape = Gaussian
# Resolution of the generated spectrum. Total number of points.
SpectrumNPoints = 1000
REACTIVITY_EN
This section is defined as following:
[REACTIVITY_EN]
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis = cc-pVTZ
# Methods to be used for the reactivityEN calculation. Options: only SP_WF methods.
Method = BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T)
# PNO setting for DLPNO method
PNOSetting = Normal
# Switch off solvation for reactivityEN, even if the optimization and other methods used solvation. This depends on how the method has been calibrated
SwitchOffSolvation = True
# Reference values for Chi and Eta for fluorine radical. The following is for DLPNO-CCSD(T) and BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) with cc-pVTZ basis set and NormalPNO in gas phase
# Chi_Ref = 11.1744
# Eta_Ref = 9.0421
# The following reference values are for BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) with cc-pVTZ basis set and NormalPNO in gas phase
# Chi_Ref = 11.2078
# Eta_Ref = 9.078
# The following reference values are for BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) with cc-pVTZ basis set and NormalPNO in water
Chi_Ref = 11.1719
Eta_Ref = 4.9929
CONFORMATIONAL_SEARCH
This section is defined as following:
[CONFORMATIONAL_SEARCH]
# Options: True, False
DoConfSearch = False
# Options: True, False
DoConfSearchTS = False
# Which program / method to use for conformer generation? Options:
# CREST, CRESTFF, RDKit, CREST-RDKIT, CRESTFF-RDKIT, GOAT, GOATFF
Conformer_Generation = CREST
# Use initial filtering step. Can be useful when reading conformers that are not filtered for rotamers.
# Options: True, False
InitialFiltering = True
# Maintain the original stereochemistry from the input file given?
FilterChiral = False
# Use preoptimization step. Options: True, False
PreOpt = True
# Options: see weasel -h
PreOpt_Method = XTB
# Use looseOpt, a second preoptimization step, using LooseOpt level method and Basis. Options: True, False
LooseOpt = False
# Options: see weasel -h
LooseOpt_Method = r2SCAN-3c
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis.
# Not used if composite methods are used, but needed in case a non-composite method is chosen.
LooseOpt_Basis = def2-TZVP(-F)
# Use optimization step. Options: True, False
Opt = True
# Options: see weasel -h
Opt_Method = r2SCAN-3c
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis.
# Not used if composite methods are used, but needed in case a non-composite method is chosen.
Opt_Basis = def2-TZVP(-F)
# Use strict convergence criteria during the Opt step?
Opt_StrictConvergence = False
# Use DFT SP energy calculation step. Options: True, False
SP_DFT = True
# Options: see weasel -h
SP_DFT_Method = wB97X-V
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
SP_DFT_Basis = def2-TZVP
# Use Post-HF SP energy calculation step. Options: True, False
SP_WF = False
# Options: see weasel -h
SP_WF_Method = DLPNO-CCSD(T)
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
SP_WF_Basis = def2-TZVP
# Use Post-HF SP energy calculation step. Options: True, False
SP_WF = False
# Options: see weasel -h
SP_WF_Method = DLPNO-CCSD(T)
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
SP_WF_Basis = def2-TZVP
# Use Gibbs free energy correction from frequency calculation when evaluation Opt, SP_DFT and SP_WF steps. Options: True, False
GibbsCorrection = False
# If frequency calculation is carried out, rerun optimization in case (unwanted) imaginary modes are found with the
# frequency analysis. If frequency calculation is not carried out, this keyword is ignored.
# Options are: True, False
CorrectImagModes = False
# What is the number of conformer generations that should be carried out? Options: integer
ConfGen_NRuns = 2
# If ConfGen_NRuns is larger than 1, generate different structures as input for the multiple ConfGen-Runs using RDKit
ConfGen_PreSeed = True
# What is the upper limit of conformers that should be considered during conformer generation? Options: integer
ConfGen_MaxNConf = 10000
# Maximum number of conformers generated with RDKit. Allowed values: -1 and >=1.
# By default (represented by: -1) the number of conformers generated is the square of the number of atoms
ConfGen_MaxNConfRdkit = -1
# What maximum energy range (kcal/mol) should be considered during conformer generation? Options: float
ConfGen_MaxEn = 6
# What minimum RMSD between different conformers should be considered during conformer generation? Options: float
ConfGen_MinRMSD = 1
# What energy range (kcal/mol) of conformers should be kept after intialfiltering? Options: float
ConfGen_EnRange_InitFilter = inf
# What energy range (kcal/mol) of conformers should be kept after preoptimization? Options: float
ConfGen_EnRange_PreOpt = 6
# What energy range (kcal/mol) of conformers should be kept after loose optimization? Options: float
ConfGen_EnRange_LooseOpt = 6
# What energy range (kcal/mol) of conformers should be kept after optimization? Options: float
ConfGen_EnRange_Opt = 5
# What energy range (kcal/mol) of conformers should be kept after DFT SP energy calculation? Options: float
ConfGen_EnRange_DFT = 4
# What energy range (kcal/mol) of conformers should be kept after Post-HF SP energy calculation? Options: float
ConfGen_EnRange_WF = 3
# Keep all rotamers coming from CREST in the ensemble?
ConfGen_KeepRotamers = False
# Which conformers to keep for actions after the ConfSearch. Options: "lowest", "all"
Conf_Keep = lowest
# What is the upper limit of conformers that should be stored / kept at the end of the conformer search? Options: integer
ConfSearch_MaxNConf = 200
# Energy difference between conformers in kcal/mol. What is the energy difference for two structures being different conformers?
Conformers_EDiff = 0.1
# RMSD in Ang. What is the RMSD for identical structures?
Conformers_RMSD = 0.125
# Method to use when computing the RMSD during the filtering step. Default is "graph", but "RDKit" and "basic" are also available but are not generally recommended.
Conformers_ScreeningRMSDMethod = graph
# Relative rotational constant threshold in %. What is the max relative rotational constant difference that distinguishes between two rotamers?
Rotamers_RelRotConstant = 1
# Threshold for rotational constant below which we still try an optimal atom mapping before the RMSD to detect rotamers. If the RMSD after the mapping is lower than "Conformers_RMSD", we consider the structures to be rotamers. Only used for the "basic" screening method.
Rotamers_RelRotConstant_Max = 5
# True if the topology of the bonds of the core atoms of the TS should not change during the TS confSearch. Only used for the "basic" screening method.
KeepTSCoreTopology = True
# Coordinates whose cumulative contributions to the TS mode exceed this threshold are considered in the TS core
TSCore_SumThreshold = 0.7
# Coordinates whose absolute contribution to the TS mode exceed this threshold are also considered in the TS core
TSCore_WeightThreshold = 0.1
# If True, internal coordinates that make up the TS core may be either dihedrals OR bonds+angles, not all three
TSCore_SeparateDihedrals = True
# RMSD in Ang. What is the RMSD of the core atoms for identical TS core structures?
Conformers_RMSD_TSCore = 0.5
# True if a second TS optimization should be carried out in case the first one fails. Necessary for super complete TS conformer set.
SecondTSOpt = False
# Percentage of how much the bonds of the core atoms of the TS can change during optimization.
Tolerance_TSCoreBonds = 15
# Run frequency calculation on lowest-energy TS conformer for TSConfSearch. Options: True, False
finalTSFrequency = True
# Do Clustering after preoptimization. Options: True, False
Conf_Use_Clustering = True
# Mode of Clustering. Options: fine, coarse
Conf_Clustering_Mode = fine
# Maximum nr of cluster. Options: integer, -1 means there is no limit
Conf_Clustering_NMax = -1
# What energy level is used for clustering. Options: PreOpt, Opt
Conf_Cluster_ELevel = PreOpt
# Method to use when computing the RMSD during the clustering step. Default is "graph", but "basic" and "hungarian" are also available
Conf_Cluster_RMSDMethod = graph
# Ignore H atoms for conformer screening and clustering.
# Options:
# * False
# * True
IgnoreHs = False
# Try to recover a non-converged SCF calculation on a conformer in the conformer search procedure by using different
# SCF accelerators strategies (for more details see the setting 'BadConvLevel' below).
# This setting only affects the conformer search procedure and trumps the global
# 'SCF_CONVERGENCE->Retry' setting.
# Options:
# * <Blank> : Use the same value as set for 'SCF_CONVERGENCE->Retry'.
# * True : Allow for SCF retries.
# * False : Do not allow to retry SCF calculation.
SCFRetry =
# Try to converge a non-converged geometry optimization by running a few more optimization cycles.
# This settings only affects the conformer search procedure and trumps the global 'Opt->Retry' setting.
# To turn on specific SCF accelerators used the setting: SCF_CONVERGENCE->BadConvLevel
# Options:
# * <Blank> : Use the same value as set for 'Opt->Retry'.
# * True : Turn on retrying.
# * False : Turn off retrying.
OptRetry =
# Generate conformers for noncovalently bound complexes. Currently only works together with CREST.
# Allowed options:
# * True
# * False
GenNCI = False
# Print files with RMSD of conformers after preoptimization and optimization step in conformational search.
# Allowed options:
# * True
# * False
PrintRMSD = False
# The conformation search will be done using the mirror image of the input molecule.
# Allowed options:
# * True
# * False
UseEnantiomer = False
GOAT
This section is defined as following:
[GOAT]
# Set GOAT-EXPLORE option for a complete search with free topology.
GOAT_Explore = False
# Set GOAT-ENTROPY option to enforce convergence of conformational entropy.
GOAT_Entropy = False
# Set GOAT-DIVERSITY option to focus on geometrical diversity.
GOAT_Diversity = False
# Set GOAT-REACT option to allow for full PES search (still experimental!).
GOAT_React = False
#Define the maximum topological difference for a GOAT-REACT run (default 8 - still experimental!).
GOAT_MaxTopoDiff = 8
# Define the number of workers used in the GOAT. Leave as -1 for an automatic assignment.
GOAT_NWorkers = -1
# Free topology between different fragments
GOAT_FreeFrag = False
# Freeze cis/trans amide chirality change when using GOAT.
GOAT_FreezeAmides = False
# Freeze cis/trans double bond chirality change when using GOAT.
GOAT_FreezeCisTrans = False
CREST
This section is defined as following:
[CREST]
# Disable CREST's default genetic crossing at the end of the iMTD-GC algorithm
CREST_NoCrossing = False
# TODO Jeko: Add comments, describing the options!!!
CREST_sMTD = False
CREST_GFN_level = 2
CHEMICAL_SEARCH
This section is defined as following:
[CHEMICAL_SEARCH]
# Method to be used for Chemical Space search.
# Options:
# * Crest
# * Docker: Currently only supports protonation.
Method = Crest
# What maximum energy range (kcal/mol) should be considered during generation of chemical compounds? Options: float
ChemSpaceGen_MaxEn = 30
# Search for tautomeric structures
TautomerSearch = False
# Search for protonated structures
ProtomerSearch = False
# Search for anion = conjugated base structures
AnionSearch = False
# Search for H-atom abstracted structures
HATSearch = False
# Search for ion binding site
IonBindingSiteSearch = False
# Filter out topologically equivalent structures based on their canonical SMILES string.
SmilesFiltering = True
CHEMICAL_SEARCH_DOCKER
This section is defined as following:
[CHEMICAL_SEARCH_DOCKER]
# These options only applied to ORCA's Docker when used as method for ProtomerSearch
# > Bonding factor applied to the sum of the covalent radii of two atoms
BondFactor = 1
# > Only keep the lowest MaxNumProtomers protomers
MaxNumProtomers = 100000
# > Docking preset.
# > The preset determines the internal parameters used to search for host-guest candidates.
# > Options: Normal, Quick, Screening or Complete
DockLevel = Quick
# TODO: Options not implemented yet!
# Options: DiffEvolution, ParticleSwarm or MutableParticleSwarm
;Algorithm = ParticleSwarm
# Options: DefMethod, ClosestAtomToOrigin, ClosestAtomToHost, GFNXTB1, GFNFXTB, GFNFF
;EvPES = GFNFXTB
# Options: NormalOpt, ReducedOpt
;OptQuality = NormalOpt
EXCITED_STATES
This section is defined as following:
[EXCITED_STATES]
# Options: True, False
DoTDDFT = False
# Spectrum part
# Plot UVVis spectrum. Options: True, False
PlotUVVis = True
# Plot CD spectrum in length representation. Options: True, False
PlotCD_length = True
# Plot CD spectrum in velocity representation. Options: True, False
PlotCD_velocity = False
# Number of roots for SP_DFT calculation. Not used for optimization. Integer
NStates = 20
# Use TDA approximation
TDA = True
# Cutoff (in %) for printing peak / excited state contributions
PrintPeak = 1
# If the current TDDFT calculation does not reach a certain wavelength, additional TDDFT calculations will be performed in order to reach that range
DoAutoExtendNStates = False
# Wavelength (in nm, should be integer) that should be reached with TDDFT calculation. If the current calculation does not reach that wavelength,
# more TDDFT calculations will be performed with AutoExtendNStatesBy additional roots, until MAX_NStates is reached.
RangeSpectrum = 300
# Number of roots that the calculation is extended by in case RangeSpectrum is not reached. This is done until AutoExtendMaxNStates is reached.
AutoExtendNStatesBy = 20
# If the current TDDFT calculation does not reach a certain wavelength, additional TDDFT calculations will be performed in order to reach that range.
AutoExtendMaxNStates = 100
# Excited state optimization part
# Do optimization on excited state level. Options: True, False
DoOpt = False
# When optimizing on ES level, follow this excited state.
# For SP calculations this is the state for which the energy is stored.
# Integer
StateNr = 1
# When optimizing to the excited state structure, use the triplet excited state. Options: True, False
# Only applicable for singlet ground states / closed shell systems
OptTriplet = False
# How many extra states on top of StateNr to include for TDDFT optimization. Only used for optimization. Integer
NExtraStates = 5
# Compute Spin-Orbit-Coupling. Options: True, False
DoSOC = False
# Indicate for which roots to compute various properties, e.g. gradients, population analysis, ...
# Options: All, or specific numbers as follows
# 1 root 1, i.e. the lowest root
# or
# 1,3,7 roots 1 and 3 and 7. States should be separated by comma.
AnalyzeStates = All
# Which density should be used for charge and bond order analysis.
# Options: <blank>, Unrelaxed, Relaxed, Both (=Unrelaxed and Relaxed)
DensityAnalysis = Unrelaxed
IR
This section is defined as following:
[IR]
# Options: True, False
DoIR = False
# Options: True, False. Implies DoIR
DoRaman = False
# Options: True, False. Implies DoIR
DoVCD = False
# Multiply harmonic frequencies by this factor before generating plots
ScaleFreq = 1.0
NMR
This section defines the types of NMR that are computed by default (H, C, N, P, Si). The default reference molecules for the chemical shift prediction, as well as the method for optimizing them, are defined here.
This section is defined as following:
[NMR]
# Compute NMR chemical shifts and/or J-couplings. Options: True, False
DoNMR = False
# Compute chemical shifts for a comma-separated list of elements (e.g.: H,C) or ALL for all elements in the system.
# Reference shieldings/molecules for all chosen elements must be provided!
Shifts = H,C
# Chemical shift references. Options: reference shielding in ppm
# or structure file (should be available in lib/references subdirectory or in the working directory).
# References for additional elements can be added as "Ref-[element]"
Ref-H = TMS.xyz
Ref-C = TMS.xyz
Ref-Si = TMS.xyz
Ref-N = CH3NO2.xyz
Ref-P = H3PO4.xyz
# Compute indirect spin-spin couplings for a comma-separated list of elements (e.g.: H,P) or ALL for all elements in the system
Coupling =
# Method for NMR coupling calculations. Recommended: PBE0
Coupling-Method = PBE0
# Basis for NMR coupling calculations. Recommended: pcJ-1/2/3
Coupling-Basis = pcJ-2
# Neglect J-couplings between atoms further apart than this threshold in Angstrom
Coupling-RThresh = 5.0
# Whether to attempt to find rotationally equivalent nuclei and average their shieldings, shifts, and couplings. Options: True, False
AverageEquivalent = True
# Spectrometer frequency (MHz) used for plotting and converting the linewidth to ppm
SpectrometerFrequency = 400
CCS
This section is defined as following:
[CCS]
# Options: True, False
DoCCS = False
# Options: True, False
DoCCScluster = False
# Maximum number of cycles
MaxCycles = 40
# Minimum Number of cycles
MinCycles = 8
# Number of velocity integration points
NIntVelocity = 48
# Number impact parameter integration points
NIntImpactParameter = 768
# Relative derivation of the standard of the mean
NFloatSEMError = 0.35
# Collision Gas. Options He, N2
Gas = N2
# CCS chargetype. CHELPG charges are most accurate for the method
ChargeType = CHELPG
REACTIVITY_NEBTS
The default settings for the NEB-TS algorithm are defined here. How many images are used for representing the minimum-energy-path? Should only the TS be computed, or the entire reaction be computed?
This section is defined as following:
[REACTIVITY_NEBTS]
# Options: True, False
DoNEBTS = False
# Fix end points of the NEBTS calculation. Do this if the end points are already optimized. Options: True, False
FixEnds = False
# Do a conformational screening of end points before starting the actual NEBTS run. Not yet functional. Options: False.
ConfScreenEnds = False
# Run, if requested, frequencies and SP energies on optimized reactant, TS and product. Options: True, False.
Compute_Full_Reaction = True
# How many images are used for the NEB run.
NImages = 8
# SLD threshold to at which structures are considered very close (WEASEL prints warning) [Angstrom]
SLDWarningThreshold = 1
# SLD threshold at which structures are considered too close (WEASEL aborts at that point) [Angstrom]
SLDErrorThreshold = 0.2
# use Fast-NEB-TS. It provides significant speedup, but at lower robustness. Options: True, False
BoostNEBTS = False
ROTATION
This section is defined as following:
[ROTATION]
# True if Rotational Barrier calculation is the default, else False
DoRotationBarrier = False
# True if TS should be computed in Rotational Barrier calculation, else False
ComputeTS = False
# Number of steps for initial scan. Options: any integer
InitialScanNSteps = 19
# Number of images for NEB calculations to compute rotational barrier between minima. Options: any integer
NImages = 8
BSSE
This section is defined as following:
[BSSE]
# Do BSSE calculation by default. Options: True, False
DoBSSE = False
# Default BSSE calculation type. Options: bsse-gCP (DFT-D3-gCP), bsse-BB (Boys-Bernardi)
Type = bsse-BB
# Default for whether the monomer geometries should be optimized or taken from the complex structure
OptimizeMonomers = True
# Default for whether a preoptimization should be performed for monomer geometries at all (optimization directly from optimized complex geometry should be quicker)
PreoptimizeMonomers = False
# Perform the BSSE part of the calculation in gas phase
BSSE_Gas = True
LED
This section is defined as following:
[LED]
# Do LED calculation
DoLED = False
# Default LED calculation type. Options: PL2019
Type = PL2019
# Default for whether the monomer geometries should be optimized or taken from the complex structure
OptimizeMonomers = False
# Default for whether a preoptimization should be performed for monomer geometries at all (optimization directly from optimized complex geometry should be quicker)
PreoptimizeMonomers = False
SYSTEM
Default charge and multiplicity of the system are defined here:
[SYSTEM]
Charge = 0
Multiplicity = 1
# If ForceUHF is set to True then always an UHF calculation is performed, otherwise it is only performed if enforced via -UHF or if the Multiplicity is != 1
ForceUHF = False
# In ORCA atoms are counted starting with 0. Weasel can start counting at 0 or 1. Options: 0, 1.
StartIndexingAtoms = 1
# In ORCA MOs are counted starting with 0. Weasel can start counting at 0 or 1. Options: 0, 1.
StartIndexingMOs = 0
# Temperature of the system in Kelvin. Options: float
Temperature = 298.15
# Pressure of the system in atm. Options: float
Pressure = 1.0
# Perform a Boltzmann-weighted average of computed properties and spectra
BoltzmannAverage = False
# Bond detection. Options: distance, XTB-BO (bond order based on XTB-SP calculation)
BondDetection = XTB-BO
# Ignore the total charged defined in settings/workflow or in the command line and take the charge info from the file.
# Only applies to SMILES.
# Allowed values: 'False' [default] or 'True'
EnforceFileCharge = False
QMMM
This section is defined as following:
[QMMM]
# Cutoff in Ang by which the active core region is extended
ExtendActiveCoreBy = 5
# When extending the core region, extend by sidechains or backbone groups separately if at least one
# atom of the respective group is within ExtendActiveCoreBy Ang. of any active core atom
ActiveRegionUseSidechainAndBackboneSeparately = True
# When extending the core region, extend by full residue if at least one atom of the residue is within
# ExtendActiveCoreBy Ang. of any active core atom
ActiveRegionUseFullResidues = False
# When extending the active core region only extend to side chain atoms
ActiveRegionFixBackbone = False
# Use QM core region for definition of active core region
ActiveCoreEqualsQMCore = True
# Use QM region for definition of active region
ActiveRegionEqualsQMRegion = False
# When extending the active core region only extend to water and hydrogen atoms
ExtendActiveCore_WAT_and_H_only = False
# When extending the active core region only extend to hydrogen atoms
ExtendActiveCore_H_only = False
# Types for cutting residue backbones in active core and region. Options are chemical
# (CaH-NH of current residue plus C=O of neighboring residue) and residueDefinition (C=O-CaH-NH of current residue)
ActiveRegionCutBB = chemical
# Cutoff in Ang by which the QM core region is extended
ExtendQMCoreBy = 3
# Cutoff in Ang by which waters are added to the QM core region if QM core region (between non-H/-C and O(WAT))
ExtendQMCoreByWaterBy = 4
# Before extending the QM core region, waters that have a certain O(WAT) - non-H/-C distance (<ExtendQMCoreByWaterBy)
# can be added to the QM core region
QMCoreAddWaterToCore = False
# When extending the core region, extend by full residue if at least one atom of the residue is within
# ExtendQMCoreBy Ang. of any active core atom
QMRegionUseFullResidues = False
# When extending the core region, extend by side chains only. For this to happen at least one atom of the
# residue's side chain is within ExtendQMCoreBy Ang. of any active core atom
QMRegionUseSideChainsOnly = False
# When extending the core region, extend by polar groups only. For this to happen at least one atom of
# a side chain or backbone is within ExtendQMCoreBy Ang. of any active core atom
QMRegionUsePolarGroupsOnly = False
# When extending the core region, extend by polar interactions only. For this to happen at least one non-H
# or non-C atom of a side chain or backbone is within ExtendQMCoreBy Ang. of any non-H or non-C active core atom
QMRegionUsePolarInteractionsOnly = False
# Check QM and MM regions and automatically correct if there are any MM gaps that are too small. In such a case
# the charge-shift schemes might become unphysical, and the QM-QM interaction between separated QM regions might become erroneous.
QMRegionAutoCorrection = True
# File extensions for files recognized as parameter and stream files for CHARMM force field conversion in the settings subdirectory
PRMLibFile_extension = prm, str
# Path where the files for CHARMM force field conversion are stored. If None is given, then the lib/forcefields directory is used.
PRMLibPath = None
# Allow solvent - of set to False, gas phase settings are enforced
AllowSolvent = False
INPUT
This section is defined as following:
[INPUT]
# Keep the topology of the input structure(s), i.e. the atom connectivity and the bond orders.
# If input structure contains no such information, it will be generated on-the-fly.
# Allowed values: 'True' or 'False'
KeepTopology = True
OUTPUT
The energy unit that is used in the summary file is defined here. The charge type, that is used for storing atomic charges in structure files, is defined here. Should large job files in the task directories be compressed? What should happen, if a mainjob directory with the same name exists at simulation start? Overwrite, or abort the calculation?
This section is defined as following:
[OUTPUT]
# Options are Eh and kcal/mol
EnergyUnit = kcal/mol
# Defines which charges are printed in the mol2 file. Options are Mulliken, Loewdin, CHELPG, Hirshfeld
ChargeType = Hirshfeld
# Defines whether charges should be stored in a file basename_charges.txt
StoreCharges = False
# Choose a compression mode or disable compression completely.
# Allowed values: <Blank>, Files, Folders
# * <Blank> : Turn off compression (i.e. leave right side of equal sign blank!)
# * Files : Only compress large files, e.g. ORCA's '.gbw' or '.out' files.
# * Folders : Compress all subfolders of the mainjob dir into a tar-ball.
Compression =
# Overwrite existing data. Options: True, False. If set to False the program will abort if the folder with data exists
Overwrite = True
# Write an unmodified copy of the input file to the main job directory (options: 'True' or 'False') [default: True]
Copy_Input = True
# Write a copy of the unoptimized 3-dimensional structure of a SMILES input to the main job directory
# (options: 'True' or 'False')
Write_3D_SMILES = True
# Write a copy of the unoptimized 3-dimensional structure of a InChI input to the main job directory
# (options: 'True' or 'False')
Write_3D_InChI = True
# Define mol-file version for the output of SDF files. Allowed values: V2000, V3000
MOL_VERSION = V3000
# Print unique SMILES of structure in "STRUCTURE FILE" block
# (options: 'True' or 'False')
PRINT_USMILES = True
# Print InChI of structure in "STRUCTURE FILE" block
# (options: 'True' or 'False')
PRINT_INCHI = False
# Write the final results in (ensemble) XYZ format
Write_XYZ = True
# Write the final results in (ensemble) SDF format
Write_SDF = False
# Write the final results in (ensemble) MAE format
Write_MAE = False
# Store wfx and wfn files for SP_DFT calculations
# (options: 'True' or 'False')
StoreWFX = False
# Verbose storage of data in summary file
VerboseSummary = False
NMS
This section is defined as following:
[NMS]
# Do Normal Mode Sampling
DoNMS = False
# Number of structures to be generate. By default it will be equal to the number of atoms
NStruc = 0
# Number of modes to be used. Default is all. If a number is given, these will be randomly chosen before compute each displacement.
NModes = 0
# Temperature to be used for the NMS
Temp = 298.15
# Unit of the the normal modes (regular, dimensionless)
Unit = dimensionless
# Use Gaussian weights?
UseGaussianW = False
# Sigma value for the Gaussian weight (in cm-1)
Sigma = 200
# Minimum frequency of mode to include (in cm-1)
MinFreq = 15
QM_DATA
This section is defined as following:
[QM_DATA]
# energies and gradients of structures from the optimization trajectory can be stored.
# Counting starts from 1 (not 0)
# 1 step 1 is stored
# or
# 1,3,7 steps 1 and 3 and 7 are stored. Steps should be separated by comma.
ConfOptStoreSteps =
BEE
This section is defined as following:
[BEE]
# Path to a custom config file for Bee
# This option is not optional, it may be left unset, though.
CustomConfigFile =
DOCKING
This section is defined as following:
[DOCKING]
# Toggle dock_guest_files workflow.
DoDock = False
# Path to a xyz file with one or multiple guest structures.
# If comment line contains exactly two integers,
# then the first one is interpreted as total charge and the second as multiplicity.
Guest =
# Charge of the guest(s). All guests are assumed to have the same charge.
# Options:
# * <Blank>
# * any integer value
GuestCharge =
# Multiplicity of the guest(s). All guests are assumed to have the same multiplicity.
# Options:
# * <Blank>
# * any integer value >= 1
GuestMultiplicity =
# How often should the guest be added.
# Options: Any integer value >=1
GuestNRepeat = 1
# Add guests sequentially.
# Options: 'True' or 'False'
GuestCumulative = True
# Bonding factor applied to sum of the covalent radii of two atoms.
# No value means using ORCA's default.
# Options: <Blank> = Let ORCA decide
# or any value >0.0
BondFactor =
# Maximum number structures to keep for optimization.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * any value >=1
MaxNumStructures =
# Sort out structures before optimization that have a higher energy than this.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * any value >0.0 (Unit: kcal/mol)
EnergyRange =
# Keep the geometry and the internal topology of the host constant.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * True
# * False
FixHost =
# Level of sophistication used for Docking.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * Normal
# * Quick
# * Screening
# * Complete
DockLevel =
# Algorithm use to generate host-guest candidate complexes
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * DiffEvolution
# * ParticleSwarm
# * MutantParticleSwarm
Algorithm =
# Method used for single point calculations.
# Options:
# * <Blank> = Let ORCA decide
# * DefMethod
# * ClosestAtomToOrigin
# * ClosestAtomToHost
# * GFNFXTB (= GFN2-xTB)
# * GFNXTB1 (= GFN1-xTB)
# * GFNFF
EvPES =
# Criteria used for geometry optimization.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * NormalOpt
# * ReducedOpt
OptQuality =
# Toggle clustering of host-guest candidate complexes.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * True
# * False
DoClustering =
SOLVENT
The solvent model and solvent (or gas phase) are defined here:
[SOLVENT]
# > implicit solvation method
# Options: CPCM, SMD
Method = CPCM
# Options: Gas, Water, Protein, Acetonitrile, Acetone, Ammonia, Ethanol, Methanol,
# CH2Cl2, CCl4, DMF, DMSO, Pyridine, THF, Chloroform, Hexane, Toluene
Solvent = Water
SOLVENT_EXPLICIT
This section is defined as following:
[SOLVENT_EXPLICIT]
# Toggle explicit solvation procedure.
DoExplicitSolvation = False
# XYZ file of solvent molecule (can also be taken from the default solvents list)
ExplicitSolvent = Water
# Method for explicit solvation.
# Options: Stochastic, Docking
Method = Stochastic
# Number of solvents molecule to add.
# Values has to be an integer, equal or larger than 1.
NumSolvents = 1
# Total charge of solvent.
# Allow values: Any integer value.
Charge =
# Multiplicity of solvent.
# Allow values: Any integer value >= 1.
Multiplicity =
# Keep the geometry and the internal topology of the solute fixed.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * True
# * False
FixSolute =
# Set a fixed radius [Angstrom] for the solvation shell
MaxRadius =
# Enforce spherical arrangement of solvent molecules around solute.
# Options:
# * <Blank> (= Let ORCA decide)
# * True
# * False
Droplet =
SOLVENT_EXPLICIT_OPT
This section is defined as following:
[SOLVENT_EXPLICIT_OPT]
# Settings concerning high level optimization performed after explicit solvation
########################################################################
# Turn optimization on/off.
# Options:
# * True
# * False
DoOpt = False
# Options BP86, B3LYP, B3LYP, MP2, XTB, ... see methodOpt
Method = r2SCAN-3c
# Options: see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis = def2-TZVP(-F)
# Options: None (no basis2 for optimization) or see [SP_WF] Basis
Basis2 = def2-TZVP
# Use the default grid (<BLANK>) or a finer grid (DefGrid3) for the optimization. Options: DefGrid1, DefGrid2, DefGrid3
Grid =
# Which thresholds to use for optimization. Options are: Loose, Normal, Tight, VeryTight
OptType = Normal
ENSEMBLE_THERMODYNAMICS
This section is defined as following:
[ENSEMBLE_THERMODYNAMICS]
# Calculate the thermodynamic state functions for the lowest conformer structure
StateFunctions = False
TRAH
This section is defined as following:
[TRAH]
# Turning on ORCA's AutoTRAH feature, which switches to TRAH-SCF if other SCF methods don't work.
# Options:
# * <Blank>: Use ORCA default.
# * False: Turn AutoTRAH off.
# * True: Turn AutoTRAH on.
AutoTRAH =
# Number of SCF iterations after which ORCA's checks if it should switch to TRAH-SCF.
# Options:
# * <Blank>: Use ORCA default.
# * <any integer >= 1>: The number of cycles after which to check if TRAH-SCF is should be used.
AutoIter =