Host-Guest interaction
The host-guest interaction workflow in WEASEL can be used to study molecular interactions between a host complex and a guest molecule using the Local Energy Decomposition (LED) tool.
Explanation
Local Energy Decomposition (LED) is a method used in computational chemistry to analyze the interaction energy between molecules. It provides a way to decompose the total interaction energy into individual contributions from different fragments or regions of the molecules involved. LED allows the detailed study of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, and electrostatic interactions.
Note
This workflow differs from the InteractionEnergy workflow in that here LED data is automatically generated, which requires some different steps.
In this tutorial we will focus on the interaction energy between methanol and two water molecules as an example.
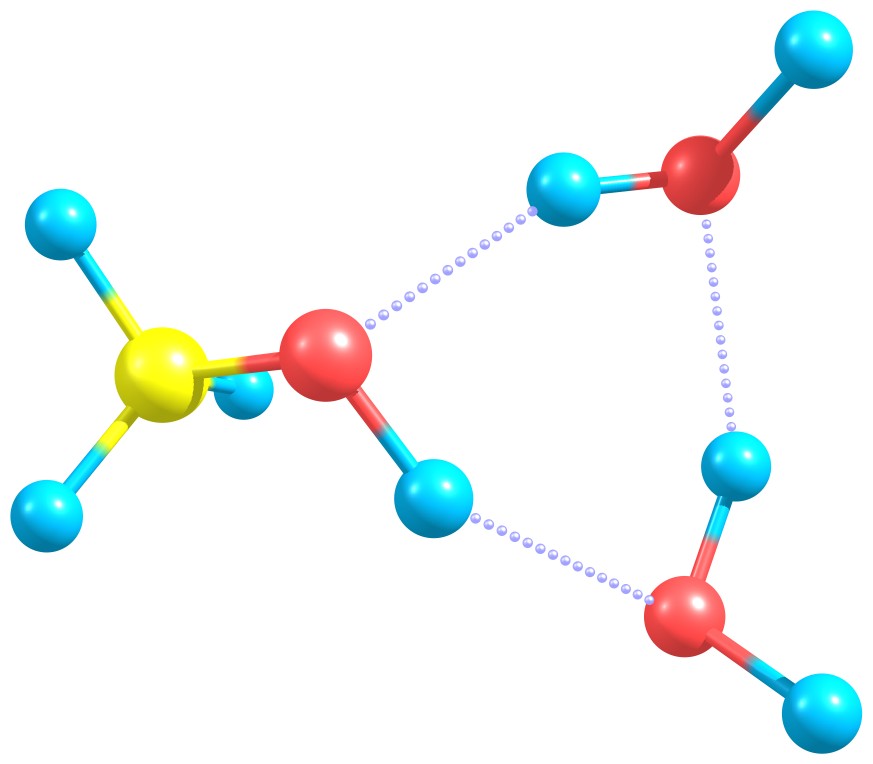
Methanol interacting with two water molecules.
How to run the calculation
To use the Host-Guest interaction workflow, you can test the mechanics using the following tutorial.
First, download and save the file wat2MeOH.xyz containing the XYZ coordinates
in the directory where you want to run your computation.
Note
WEASEL recognizes the molecules of the host structure by detecting bonds based on simple distance criteria.
If the structure is provided via a .mol2 file, the bond information in the .mol2 file is used.
Important
The host-guest interaction workflow can be used for host-guest complexes with an unlimited number of monomers. The last monomer in the structure file is used as the guest structure.
Then open a command prompt or terminal. Use the following command to start the workflow:
weasel wat2MeOH.xyz -W HostGuestLED
This will start the host-guest interaction workflow in WEASEL, specifically using the LED method to analyze the interaction energy between the host (methanol) and the guest molecules (two water molecules).
Steps of the WEASEL workflow
The workflow consists of several steps that are performed automatically by WEASEL. Let's go through the workflow steps:
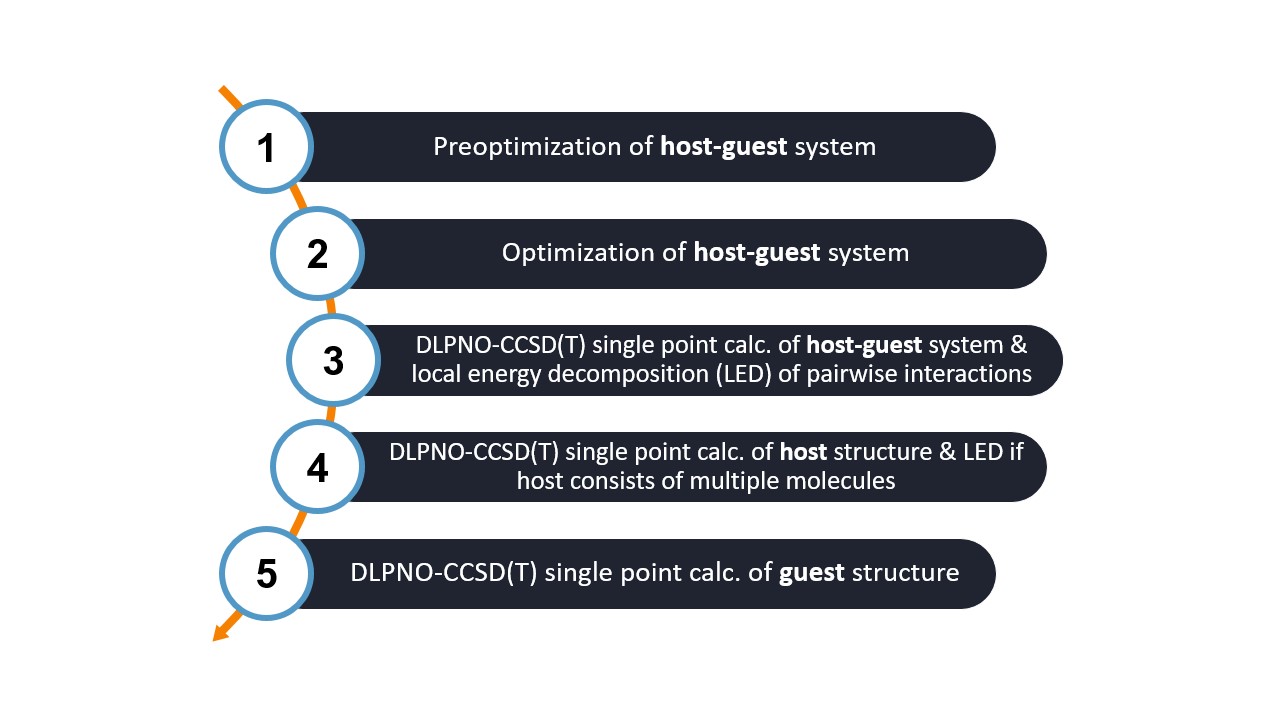
Step 1: Prior to the main optimization, a preoptimization step is performed using the semi-empirical GFN2-xTB method. This step helps to generate reasonable initial geometries for the host-guest system.
Step 2: The host-guest system is optimized using the comosite r2SCAN-3c DFT function. This optimization step adjusts the positions of the atoms in the system to find a stable and energetically favorable configuration.
Step 3: A single point calculation is performed using the BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) WF method to obtain an accurate interaction energy. In addition, the LED analysis is performed to examine the contributions of different fragments or regions within the host-guest complex.
Step 4: A separate single point calculation using the BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) method is performed specifically for the host molecule(s). If the host consists of multiple molecules, the LED analysis is also performed to analyze the interactions between the host molecules.
Step 5: A single point calculation at the BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) level is performed for the guest only.
Note
By default, the calculation is performed in the gas phase. However, you can change the settings to include a solvent if desired.
That's it! You now have an overview of the HostGuestLED workflow in WEASEL.
Output files and results
The HostGuestLED workflow generates several files that provide information about the calculation and results:
.
├── wat2MeOH.xyz
└── wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED
├── wat2MeOH_HG-LED_Total.png
├── wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED.input.xyz
├── wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED.report
├── wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED.summary
├── wat2MeOH_LED-Labels.avogadro.mol2
├── wat2MeOH_LED.txt
├── wat2MeOH_Opt.xyz
├── BuildTopo
│ └── wat2MeOH_BuildTopo job files
├── PreOpt
│ └── wat2MeOH_PreOpt job files
├── Opt
│ └── wat2MeOH_Opt job files
├── SP_WF
└── wat2MeOH_SP_WF job files
File |
Description |
|---|---|
wat2MeOH_HG-LED_Total.png |
Plot with LED interaction map |
wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED.input.xyz |
Input host-guest structure |
wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED.report |
Output file of the WEASEL run |
wat2MeOH_HostGuestLED.summary |
Summary file for the WEASEL run |
wat2MeOH_LED-Labels.avogadro.mol2 |
mol2 file with , can be opened with avogadro |
wat2MeOH_LED.txt |
File with LED data separated by tabs |
wat2MeOH_Opt.xyz |
Optimized host-guest structure |
As for all WEASEL calculations, the .summary file provides an overview of all calculated energies including the interaction energy:
Energy [kcal/mol] / Value Type Calculation type Method Basis set Solvent Charge Multiplicity Further tags
-11540.013857 SP-Energy PreOpt XTB None Gas phase 0 1
-168524.490090 SP-Energy Opt r2SCAN-3c None Gas phase 0 1
-168330.643393 SP-Energy SP_WF BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) def2-TZVPP Gas phase 0 1 LED HG Geom HG
-95807.277680 SP-Energy SP_WF BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) def2-TZVPP Gas phase 0 1 LED H Geom HG
-72510.413886 SP-Energy SP_WF BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) def2-TZVPP Gas phase 0 1 LED G Geom HG
-12.951826 SP-Energy Interaction-Energy BP-DLPNO-CCSD(T) def2-TZVPP Gas phase 0 1 LED Summary WF
Structure file that can be opened with e.g. avogadro. It shows the chemical shifts as labels (*Display Settings - Label - Atom labels section, Text: Partial charge*)
WEASEL also provides automatically a visualized LED interaction map. For our studied example it looks as following:
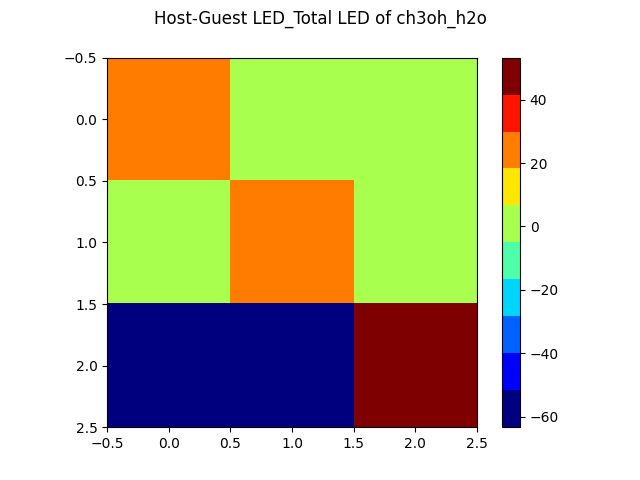
Plot with LED interaction map
Keywords and remarks
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Do host-guest LED calculation. |
|
Do not do a host-guest LED calculation (even if defined in settings). |
|
Do only the calculations for the dimer part, i.e. no monomer calculations. |
|
Host-guest LED calculation: do not separately optimize the monomers,
but instead use their geometries in the complex.
|
|
Host-guest LED calculation: separately optimize the monomers. |
|
Add guest molecule to host: Needs structure file. Optional: 1)
Charge of the guest: -C <charge> (default 0). 2) Multiplicity of the guest:
-M <multiplicity> (default 1).
|