Workflows
As we discussed in the introductory chapter, WEASEL is a powerful tool for streamlining and organizing multiple ORCA computations and processing the resulting data in a single workflow. In this tutorial, we will explore the basic structure of WEASEL's workflow, explore the use of different workflows, and become familiar with the wide range of workflows available. In WEASEL workflows are defined by ini-files using simple key-value pairs which are grouped in sections.
Basic workflow
In our first calculation, as shown in the "Hello Water" section, we used WEASEL's basic workflow to obtain the molecular structure and energy of water. This workflow consists of three main steps: preoptimization, optimization, and a DFT single point energy calculation, all performed in the aqueous solutions, and represents the basic workflow in WEASEL.
The steps of the basic workflow are shown in the following figure:
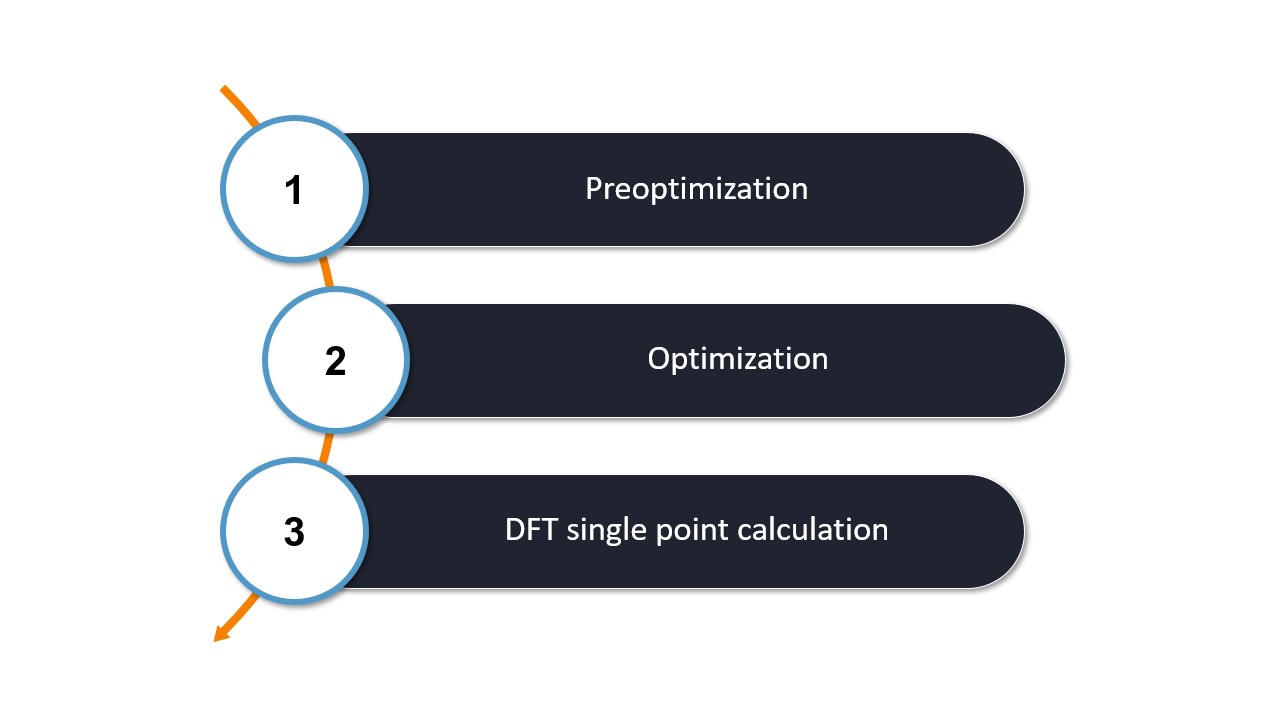
Basic workflow.
All three actions are automatically setup by WEASEL and performed with ORCA and XTB. The result of the preoptimization is used as the starting point for the optimization and the computed structure of the optimization is the one on which the single point DFT calculation is performed.
Note
WEASEL also offers a more comprehensive workflow, which is recommended to obtain more accurate energies, which includes a high-level wavefunction single point energy calculation (using the DLPNO-CCSD(T) method by default). The calculation follows the DFT single point energy calculation. By default, this task is not included in the basic workflow as it quite costly, but it can be enabled using the following command:
weasel water.xyz -spwf
Note that the basic workflow can be customized using command line keywords,
as in the example above where the keyword -spwf was used in addition to the basic workflow.
The keyword options and their use are discussed in detail in the upcoming section on command line keywords.
If you are interested in exploring how the methods for the basic workflow are defined and where they are located, you can refer to the section on settings for further insight into this topic.
Standard workflows
In addition to the basic workflow, WEASEL includes a number of advanced workflows. Such an advanced workflow is invoked in the following way. For example, the following command calls the workflow that performs a series of calculations that will eventually produce the simulation of the IR spectrum of water:
weasel water.xyz -workflow Spectrum-IR
You can also simply abbreviate -workflow to -W so that the IR spectrum simulation can be invoked via
weasel water.xyz -W Spectrum-IR
Note
When a workflow is requested, its name is added as a suffix to the stem of the input filename, e.g. water_Spectrum-IR for the above WEASEL call.
A label can be defined (-label THF) and added to the stem, e.g. water_Spectrum-IR_THF for the WEASEL call:
weasel water.xyz -W Spectrum-IR -label THF
Available workflows
The IR spectrum workflow example is just one of many standard workflows available in WEASEL. Some of the tutorials in the following chapters will use the different standard workflows to show you how you can calculate different properties, reaction mechanisms, and spectra for your systems of interest by using just one workflow keyword in WEASEL. For example, a detailed tutorial on the IR Spectrum workflow example introduced above can be found here.
The -h command line argument is short for help, and the command prints not only a complete list of all available workflows,
but also all available command line keywords with brief descriptions of their purpose.
To find the list of workflows in the help output, look for the following:
weasel -h
and the result is shown in the Workflows section:
Workflows:
Standard workflows
-workflow W, -W W Available workflows are: [...]
The list of available workflows is generated based on the available workflow settings files in your WEASEL version.
Important
To make searching for keywords easier, WEASEL also has tab completion. This means that typing weasel water.xyz -W followed by a
tab will display all options available for -W.
The following tables give you an overview on all available workflows in WEASEL 1.10 with short explanations and links to the respective tutorials if they are available, yet.
Workflows for reactivity calculations:
The reactivity workflows optimize the structures of reactants, transition states, and products in chemical reactions and determine properties such as activation and reaction energies from the energies of these structures. They provide a deeper understanding of reaction mechanisms, enable the prediction and analysis of reaction outcomes, and offer insight into the energetics of chemical reactions. A detailed tutorial on reactivity calculations with WEASEL can be found here.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow calculates the reaction and activation free energy for a
reaction between provided reactant and product.
|
|
This workflow calculates the reaction and activation free energies for
a reaction between a given reactant and product at a lower level of
theory to get quick results or a first impression of the reactivity.
|
Worklfows for interaction energies and properties:
Interaction energy workflows are dedicated to the analysis of interactions between molecules by calculating the energy contributions from interactions. These workflows can provide valuable insight into the strength, nature, and stability of molecular interactions.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow detects separate fragments (A + B) in the provided system
and calculates the interaction energy between two fragments, or between
a set of fragments and the another fragments, if more than two separate
fragments are provided. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow computes the interaction energy in a host-guest complex
using the LED DLPNO-CCSD(T) scheme. You can find the tutorial here.
|
Workflows for finding conformers:
Conformer ensemble workflows can be used to explore the different conformations and structural variations of molecules. They generate a collection of energetically accessible conformers that provide insight into the spatial arrangement of the molecule.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow yields a conformer ensemble for a system. |
|
This workflow produces a conformer ensemble specifically for the active
part of a system.
|
|
This workflow calculates a conformer ensemble for a transition state (TS). |
|
This workflow calculates displaced structures via Normal-Mode-Sampling. |
Workflows for chemical searchs:
Chemical Searcher workflows use part of the conformational workflow to find specific ensembles of chemical species, such as a conformational ensemble of potential conjugate bases of a given system.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow finds conjugate bases of a given system and obtains their
conformer ensembles.
|
|
This workflow finds the likely products for a hydrogen atom abstraction
(HAT) reaction on the system and obtains their conformer ensembles.
|
|
This workflow finds possible products for a reaction between the system
and a given cation and obtains their conformer ensembles.
|
|
This workflow finds conjugate acids of a given system and obtains their
conformer ensembles.
|
|
This workflow finds prototropic tautomers of a given system and obtains
their conformer ensembles.
|
Workflows for CCS:
The CCS workflows calcluate collision cross sections of molecular structures. You can find the tutorial here.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow calculates the collision cross section (CCS) of an input
structure.
|
|
This workflow calculates the collision cross section (CCS) after
deprotonation and conformer search.
|
|
This workflow calculates the collision cross section (CCS) after
protonation and conformer search.
|
Workflows for spectra simulation:
Spectroscopy workflows simulate and analyze spectra to predict or help interpret experimental results. WEASEL offers a selection of workflows for different spectroscopic methods as listed in the table below.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow calculates an infrared (IR) absorption spectrum of a
specific molecular structure. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates a Boltzmann-averaged infrared (IR) absorption
spectrum of a conformer ensemble. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) chemical
shifts of a specific molecular structure. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates Boltzmann-averaged nuclear magnetic resonance
(NMR) chemical shifts of a conformer ensemble. You can find the tutorial
here.
|
|
This workflow calculates infrared (IR) absorption and Raman
spectra of a conformer ensemble. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates Boltzmann-averaged infrared (IR) absorption
and Raman spectra of a specific molecular structure. You can find the
tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates UV/Vis absorption and circular dichroism (CD)
spectra of a specific molecular structure. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates Boltzmann-averaged UV/Vis absorption and
circular dichroism (CD) spectra. You can find the tutorial here.
|
|
This workflow calculates infrared (IR) absorption and VCD spectra
of a specific molecular structure.
|
Workflows for excited state properties:
Excited state workflows focus on the optimization of calculated excited states. These workflows aim to determine the electronic structure and properties of molecules in their electronically excited states, providing valuable insights into phenomena such as electronic transitions, photophysics, and photochemistry.
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
This workflow optimizes a structure in an excited electronic
state via a TD-DFT calculation.
|
|
This workflow performs a conformer search to obtain the lowest-energy
conformer and calculates calculates the coupling of the first 5 excited
states of the lowest-energy conformer to its ground state.
|
Note
In addition to the available workflows, it is also possible to invoke custom workflows.
To do this, you can use the -workflow-file keyword followed by the path to the custom file.