NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra provide valuable information about the chemical environment of atoms within a molecule. In the NMR workflow, you can predict and analyze NMR spectra. Let's explore an example using aspirin.
How to run the calculation
To calculate the NMR spectra for the aspirin example yourself,
you can either create the aspirin structure manually or download the XYZ file aspirin.xyz.
You can run the NMR calculation using the following command:
weasel aspirin.xyz -W Spectrum-NMR
Alternatively, you can use the SMILES string:
weasel -smiles 'CC(=O)Oc1ccccc1C(=O)O' -W Spectrum-NMR
Steps of the WEASEL workflow
The NMR workflow consists of the following steps:
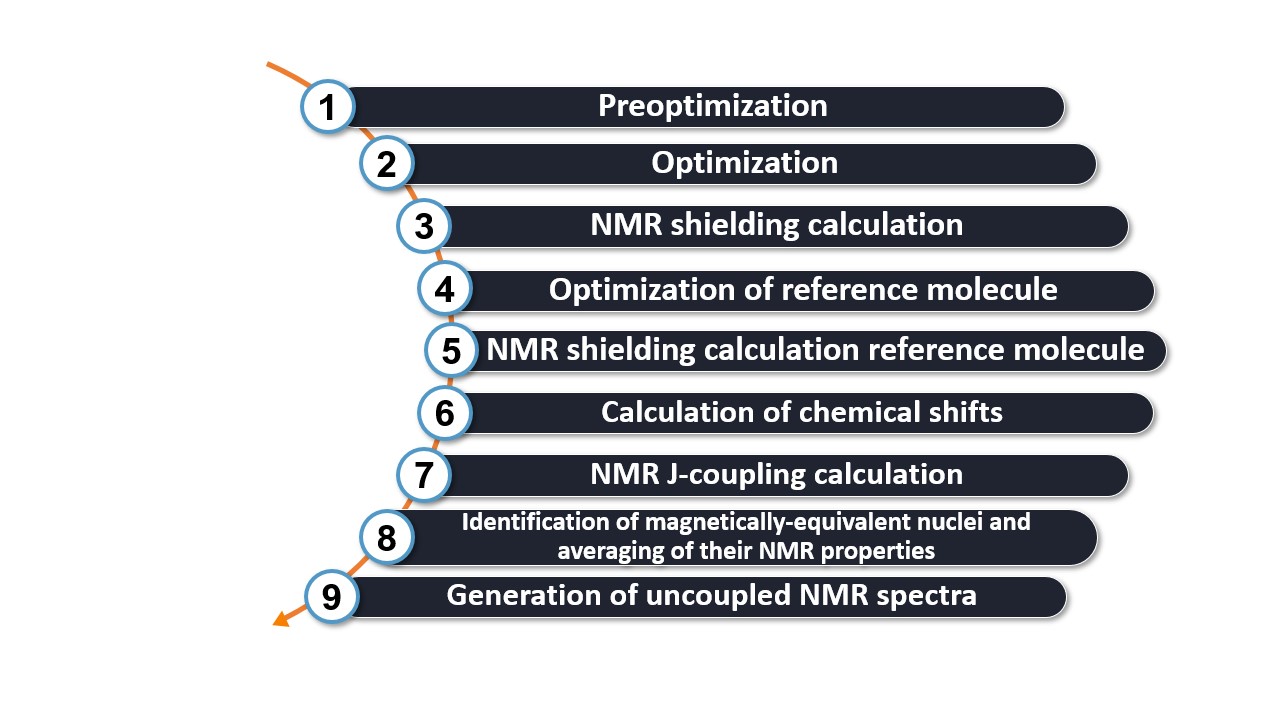
The first two steps of the workflow correspond to the basic workflow, which includes:
Step 1: Preoptimization - The molecule is preoptimized using XTB.
Step 2: Optimization - The molecule is optimized with r2SCAN-3c.
The NMR calculation is then started:
Step 3: NMR shielding calculation - The NMR shielding values for each nucleus are calculated using the B97M-D3BJ method and the pcSseg-2 basis set.
Note
You can modify the workflow by specifying different methods and basis sets for preoptimization, optimization and shielding calculations. By default, the preoptimization and optimization steps use the basic workflow methods. You can modify them according to Command line keywords.
For the NMR shielding calculation, the method and basis can be modified using the
keyword -spdft-method followed by the desired method and -spdft-basis followed by the basis set.
Since the goal of the workflow is to calculate the NMR chemical shifts and predict the entire NMR spectrum, a reference molecule is always required. This leads to the repetition of the second and third points in the workflow for the reference molecule (Step 4 and Step 5 in the workflow). In this case the pre-optimization will be skipped.
Note
The reference molecule is Tetramethylsilane (TMS) by default and is calculated at the same level as the molecule of interest. You can either change the reference molecule or provide your own reference shielding values. In the latter case steps 4 and 5 of the workflow are skipped. See below for more information.
The last steps are the calculation of the chemical shift and the generation of spectra:
Step 6: Shift Calculation - The chemical shifts are calculated as the difference between the reference shielding and the shielding of each nucleus (shift(nucleus) = shielding(reference) - shielding(nucleus).).
Step 7: NMR J coupling calculation (optional) - The NMR J-coupling values are calculated using the PBE0/pcJ-2 method.
This step is skipped by default. It can be called using the keyword -nmr-coupling followed by the nuclei you want to calculate.
Step 8: Identify Magnetically Identical Nuclei - To obtain the correct intensity in the spectrum, magnetically identical nuclei are identified and the NMR properties are averaged.
Step 9: Generate Uncoupled NMR Spectra - The data of the NMR spectra (both 1 H and 13 C by default) are generated and the spectra are visualized. The type of nuclei calculated can be changed as described below.
Note
The NMR workflow runs in the chloroform solvent. You can switch to another solvent by using the keyword
-solvent followed by the desired solvent. Potential solvents are Water, Protein, Acetonitrile, Acetone, Ammonia, Ethanol, Methanol,
CH2Cl2, CCl4, DMF, DMSO, Pyridine, THF, Chloroform, Hexane, Toluene. The concentration of the molecule in the solvent is fixed to infinite dilution.
Output files and results:
During the workflow, several files are created that are important for analyzing the results. These files are organized in a directory structure and serve different purposes:
.
├── apsirine.xyz
└── aspirin_Spectrum-UVVisCD
├── aspirin_CNMR.svg
├── aspirin_CNMR.tsv
├── aspirin_HNMR.svg
├── aspirin_HNMR.tsv
├── aspirin_NMR-Shifts.avogadro.mol2
├── aspirin_NMR.dx
├── aspirin_Opt.xyz
├── aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.input.xyz
├── aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.report
├── aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.restart.tsv.bz2
├── aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.results.xyz
├── aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.summary
├── BuildTopo
│ └── BuildTopo job files
├── PreOpt
│ └── ORCA job files
├── Opt
│ └── ORCA job files
└── SP_DFT
└── ORCA job files
Let's explore the most important files and their contents in the table below:
File |
Content |
|---|---|
aspirin_NMR-Shifts.avogadro.mol2 |
Structure file that can be opened with e.g. avogadro. |
aspirin_NMR.dx |
H- and C-NMR data in JCAMP-DX format. |
aspirin_HNMR.svg |
Visualization of H-NMR spectrum. |
aspirin_CNMR.svg |
Visualization of C-NMR spectrum. |
aspirin_HNMR.tsv |
H-NMR data in TSV format. |
aspirin_CNMR.tsv |
C-NMR data in TSV format. |
aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.report |
Report file of the workflow. |
aspirin_Spectrum-NMR.summary |
Summary of the energies of the workflow steps. |
As mentioned in the table, the 1 H-NMR and 13 C-NMR data are available in two different file formats: TSV and JCAMP-DX. The plotted 1 H-NMR and 13 C-NMR spectra are available as SVG files. Below is an example of the computed 1 H-NMR spectrum as available in the SVG file:
Predicted 1 H-NMR spectrum of aspirine.
The summary file contains chemical shifts for both 13 C and 1 H nuclei. The summary file follows a specific format, starting with the results of the basic workflow, including the PreOpt, Opt and SP DFT energies. This is followed by the shielding values of the reference compounds serving as benchmarks. Finally, the calculated shifts are listed for each nucleus. Here's an example of how the information is presented:
Energy [kcal/mol] / Value Type Calculation type Method Basis set Solvent Charge Multiplicity Further tags
-24882.379652 SP-Energy PreOpt XTB None ALPB(CHCl3) 0 1
-407011.301840 SP-Energy Opt r2SCAN-3c None CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1
-407442.473772 SP-Energy SP_DFT B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1
-281823.185647 SP-Energy Opt r2SCAN-3c None CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1 H,C-NMR reference molecule TMS - optimization
-282020.293577 SP-Energy SP_DFT B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1 H,C-NMR reference molecule TMS - shielding calculation
31.612 NMR Shielding (ppm) H-NMR_Ref_Shielding B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1 H,C-NMR reference molecule TMS - shielding calculation
187.185 NMR Shielding (ppm) C-NMR_Ref_Shielding B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1 H,C-NMR reference molecule TMS - shielding calculation
134.502 NMR Chem Shift (ppm) 1C NMR_Chem_Shift B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1
[...]
175.629 NMR Chem Shift (ppm) 12C NMR_Chem_Shift B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1
7.041 NMR Chem Shift (ppm) 14H NMR_Chem_Shift B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1
[...]
2.447 NMR Chem Shift (ppm) 21H NMR_Chem_Shift B97M-D3BJ pcSseg-2 CPCM(Chloroform) 0 1
Important
NMR Shielding is the absolute calculated value for a given nucleus, while the NMR Chemical Shift is the quantity relative to the reference, what is usually measured during experiments.
The generated structure file, aspirin_NMR-Shifts.avogadro.mol2, provides a convenient way to associate the calculated shifts with their respective nuclei. By opening this file with software such as Avogadro, you can visualize the molecule and observe the chemical shifts labeled at each nucleus. Here's an example of how the shifts are displayed:
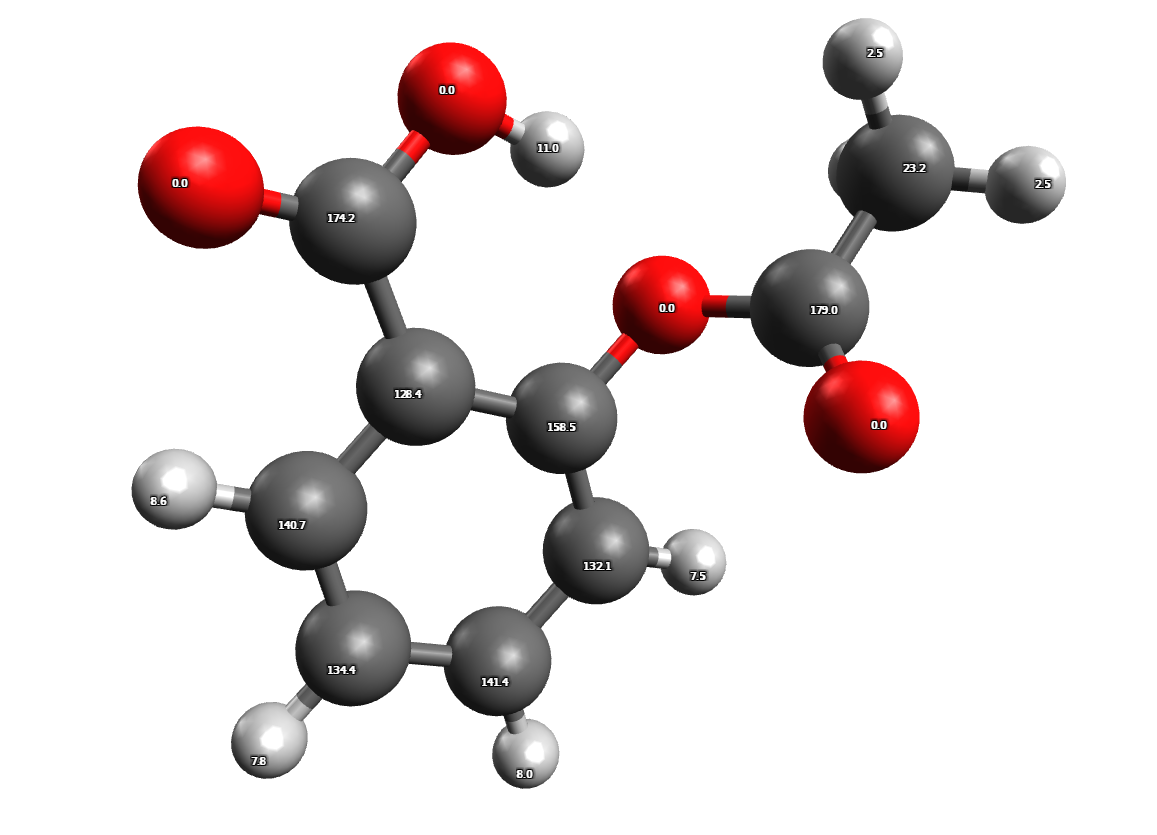
Predicted 1 H and 13 C NMR chemical shifts of aspirine
These labels allow you to easily identify and analyze the specific nuclei and their associated chemical shifts.
NMR spectrum ensemble workflow
The workflow presented is designed to handle individual molecular structures. However, it is also possible to compute a conformational ensemble, which can be particularly relevant for molecules like aspirin that can exist in multiple conformations.
To start the workflow, you can use the following command:
weasel aspirin.xyz -W Spectrum-NMR-Ensemble
You can also specify the SMILES string instead of the XYZ file, as mentioned earlier<smiles_nmr>.
The workflow differs from the single structure NMR spectrum workflow in that it incorporates a conformational search, as described in the section on Conformational Searches. For the case of aspirin, the resulting conformers are visualized below.
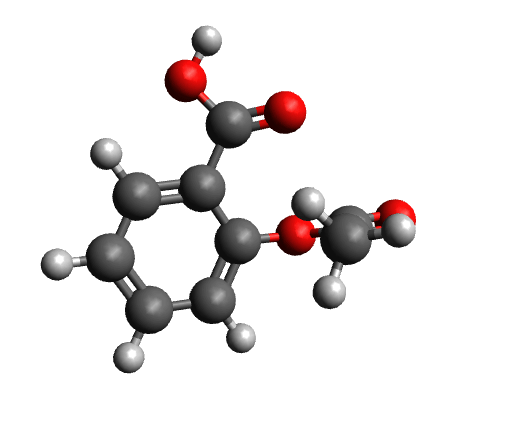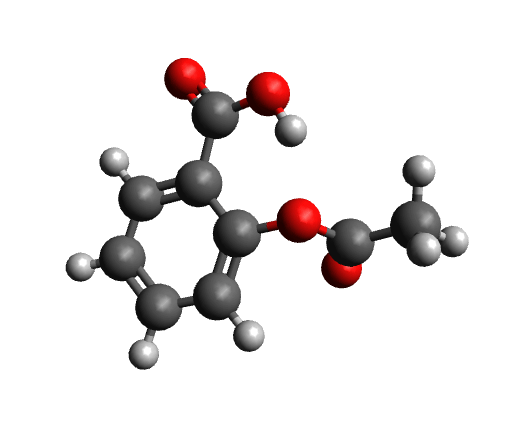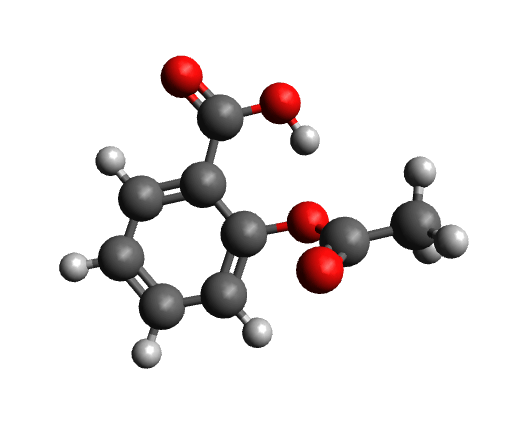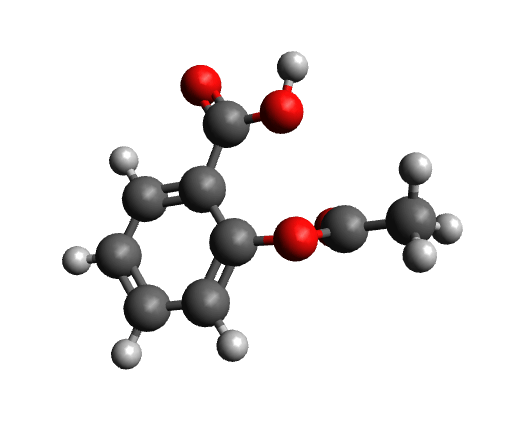
Calculated conformers of aspirin based on the conformer search workflow.
After the conformer search, the NMR spectrum of the final conformer ensemble is calculated. The resulting NMR spectra of each conformer are Boltzmann weighted, meaning that the contribution of each conformer to the final NMR spectrum is determined by its Boltzmann population.
Predicted 1 H-NMR spectrum for the conformere ensemble of aspirine.
Note
The Boltzmann weighting used in the workflow is dependent on temperature with a default value of 298.5 K. You can adjust the temperature by using the -temp keyword followed by the desired temperature in Kelvin.
Available NMR predictions
You can compute NMR properties for different types of nuclei using the following keywords:
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
-nmr H |
Compute NMR Properties of all hydrogen atoms. |
-nmr C |
Compute NMR Properties of all carbon atoms. |
-nmr N |
Compute NMR Properties of all nitrogen atoms. |
-nmr P |
Compute NMR Properties of all phosphor atoms. |
-nmr Si |
Compute NMR Properties of all silicium atoms. |
You can specify multiple nuclei to compute at the same time. For example:
weasel pyridine.xyz -workflow Spectrum-NMR -nmr H C N
predicts the NMR spectra for the 1 H, 13 C, and 15 N nuclei in pyridine.
Note
If none of the above explicit keywords is provided, by default a 1 H-NMR and 13 C-NMR prediction is carried out.
Reference molecules
ORCA can compute the absolute chemical shieldings. However, the chemical shift values printed in an experimental NMR spectrum correspond to the numerical difference between the chemical shieldings of the molecule of interest and that of the reference molecule.
WEASEL provides not only the chemical shielding of the atoms, but also their chemical shifts. To achieve this, the chemical shieldings of the reference molecule must also be calculated.
The standard reference molecules used in each NMR experiment are defined as follows:
NMR-Type |
Reference |
|---|---|
H-NMR |
TMS |
C-NMR |
TMS |
N-NMR |
CH3NO2 |
P-NMR |
H3PO4 |
Si-NMR |
TMS |
If you are using different reference molecules compared to the ones defined above, you can simply exchange them. The exchange needs to be done in two places:
Adding the new reference molecule structure file to the library
The structure files for the reference molecule are stored here:
weasel1.5
├── lib
│ ├── references
│ │ ├── CH3NO2.xyz
│ │ ├── H3PO4.xyz
│ │ └── TMS.xyz
A structure file for the added reference molecule needs to be added to this directory.
Adding the new reference molecule to the workflow settings
The new reference molecule needs to be added to the workflow configuration file. The two NMR workflow files are stored here:
weasel1.5
├── lib
│ └── workflows
│ ├── workflow_exploreNMR.ini
│ └── workflow_NMR.ini
Note
It is recommended to add a new workflow configuration file if you are changing reference molecules.
The new reference molecule needs to be added to the NMR section of the corresponding workflow configuration file. The previous reference molecule should be replaced by the name of the new reference molecule in the corresponding NMR-type key:
# Reference values for atomic chemical shieldings.
# Options: chemical shielding in ppm or structure file (should
# be available in lib/references subdirectory).
Ref-H = TMS.xyz
Ref-C = TMS.xyz
Ref-Si = TMS.xyz
Ref-N = CH3NO2.xyz
Ref-P = H3PO4.xyz
Alternatively, the absolute chemical shielding of the reference molecule can be defined at this point of the NMR section of the workflow file. This would save computational time, since the chemical shielding of the reference molecule does not need to be calculated in each simulation.
Warning
Adding the absolute chemical shielding of a reference molecule is not recommended, since then the workflow is not generally applicable any more - the reference molecule's chemical shielding can change upon solvent exchange, which would not be reflected when defining the absolute chemical shielding, and this introduces errors to the predicted chemical shift.
Remarks and keywords
Keywords related to NMR spectrum calcualtions:
Keywords for different NMR calculations methods:
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Runs NMR workflow as described above. |
|
Runs NMR workflow on ensemble as described above. |
|
Compute NMR chemical shifts for a list of elements or "all". If no element
is defined, default is H and C.
|
|
Method used for NMR J-coupling calculation. Allowed options see:
-spdft-method
|
|
Basis used for NMR J-coupling calculation. Allowed options see:
-spdft-basis
|
Keywords for different NMR calculations for different nuclei and references
Keyword |
Description |
|---|---|
|
NMR reference for H: value in ppm or structure file. |
|
NMR reference for C: value in ppm or structure file. |
|
NMR reference for N: value in ppm or structure file. |
|
NMR reference for Si: value in ppm or structure file. |
|
NMR reference for P: value in ppm or structure file. |
|
NMR reference (value in ppm or structure file) for another element.
Replace {x} with an element symbol in lowercase.
|
|
Compute NMR indirect spin-spin couplings for a list of elements or "all".
If no element is defined, default is H.
|